Configuring Cloud Scanner for Google Cloud Platform
Cloud Scanner can be deployed using one of the following:
Cloud Scanner on GCP Cloud Run
You need to configure Terraform with the appropriate resources and inputs for your particular scenario, and you will need to provide the IP address or DNS name for the ThreatMapper management console and an API key.
Copy and paste the following (single project or multiple projects) into a new file cloud-scanner.tf. Edit the fields: region, mgmt-console-url and deepfence-key.
Single Project
module "cloud-scanner_example_single-project" {
source = "deepfence/cloud-scanner/gcp//examples/single-project"
version = "0.6.0"
name = "deepfence-cloud-scanner"
# mgmt-console-url: deepfence.customer.com or 22.33.44.55
mgmt-console-url = "<Console URL>"
mgmt-console-port = "443"
deepfence-key = "<Deepfence-key>"
# GCP Project Name (Optional, for easy identification)
project_name = ""
image_name = "us-east1-docker.pkg.dev/deepfenceio/deepfence/cloud_scanner_ce:2.3.1"
# project_id example: dev1-123456
project_id = "<PROJECT_ID>"
# region example: asia-east1
region = "<REGION_ID>"
# Optional for private ip console
# Name of vpc network in which the management console was deployed
vpc = ""
# Optional for private ip console
# IP CIDR range for the connector to above vpc
# Example: 11.0.0.0/28
ip_cidr_range_svpca = ""
cpu = "2"
memory = "4096Mi"
labels = {
name = "deepfence-cloud-scanner"
}
}
Multiple Projects (Organization Deployment)
module "cloud-scanner_example_multiple-projects" {
source = "deepfence/cloud-scanner/gcp//examples/multi-project"
version = "0.6.0"
name = "deepfence-cloud-scanner"
# org_domain: root project name
org_domain = ""
# mgmt-console-url: deepfence.customer.com or 22.33.44.55
mgmt-console-url = "<Console URL>"
mgmt-console-port = "443"
deepfence-key = "<Deepfence-key>"
image_name = "us-east1-docker.pkg.dev/deepfenceio/deepfence/cloud_scanner_ce:2.3.1"
# project_id example: dev1-123456
project_id = "<PROJECT_ID>"
# region example: asia-east1
region = "<REGION_ID>"
# Optional for private ip console
# Name of vpc network in which the management console was deployed
vpc = ""
# Optional for private ip console
# IP CIDR range for the connector to above vpc
# Example: 11.0.0.0/28
ip_cidr_range_svpca = ""
cpu = "4"
memory = "8192Mi"
labels = {
name = "deepfence-cloud-scanner"
}
}
Ensure that the name parameter is set to some unique string to avoid collision with existing resource names in the project of deployment
Then run
terraform init
terraform plan
terraform apply
To connect to a private ip console on a vpc, this deployment will create a serverless vpc connector. Specify the vpc name of console and ip_cidr_range with a mask of /28 for the connector, default is 11.0.0.0/28.
For full details, refer to the examples provided in the GitHub repository: https://github.com/deepfence/terraform-gcp-cloud-scanner
Ensure that the name parameter is set to some unique string to avoid collision with existing resource names in the project of deployment
Cloud Scanner on GKE Cluster
Pre-requisite:
-
GKE cluster with workload identity enabled.
(refer here for gke documentation on how to enable workload identity)
-
gcloud cli is configured and is able to access the required project where cloud scanner will be deployed
Cloud Scanner is deployed as a pod within your GKE cluster
You need to configure Terraform with the appropriate resources and inputs for your particular scenario, and you will need to provide the IP address or DNS name for the ThreatMapper management console and an API key.
Copy and paste the following (single project or multiple projects) into a new file cloud-scanner.tf. Edit the fields: region, mgmt-console-url and deepfence-key.
Single Project Cloud Scanner on GKE Cluster with workload identity
data "google_client_config" "current" {}
# target cluster to deploy cloud scanner
data "google_container_cluster" "target_cluster" {
name = "<TARGET GKE CLUSTER NAME>"
location = "<TARGET GKE CLUSTER NAME>"
project = "<PROJECT_ID>"
}
module "cloud_scanner_example_single_project" {
source = "deepfence/cloud-scanner/gcp//examples/gke"
version = "0.7.2"
gke_host = "https://${data.google_container_cluster.target_cluster.endpoint}"
gke_token = data.google_client_config.current.access_token
gke_cluster_ca_certificate = base64decode(data.google_container_cluster.target_cluster.master_auth[0].cluster_ca_certificate,)
name = "deepfence-cloud-scanner"
# mgmt-console-url: deepfence.customer.com or 22.33.44.55
mgmt-console-url = "<Console URL>"
deepfence-key = "<Deepfence-key>"
image_name = "us-east1-docker.pkg.dev/deepfenceio/deepfence/cloud_scanner_ce"
image_tag = "2.3.1"
# project_id example: dev1-123456
project_id = "<PROJECT_ID>"
# region example: asia-east1
region = "<REGION_ID>"
# target gke cluster to deploy cloud scanner
cluster_name = "<TARGET GKE CLUSTER NAME>"
# target gke cluster location
cluster_location = "<TARGET GKE CLUSTER LOCATION>"
}
Multiple Project Cloud Scanner on GKE Cluster with workload identity
data "google_client_config" "current" {}
# target cluster to deploy cloud scanner
data "google_container_cluster" "target_cluster" {
name = "<TARGET GKE CLUSTER NAME>"
location = "<TARGET GKE CLUSTER NAME>"
project = "<PROJECT_ID>"
}
module "cloud_scanner_example_multiple_project" {
source = "deepfence/cloud-scanner/gcp//examples/gke"
version = "0.7.2"
name = "deepfence-cloud-scanner"
gke_host = "https://${data.google_container_cluster.target_cluster.endpoint}"
gke_token = data.google_client_config.current.access_token
gke_cluster_ca_certificate = base64decode(data.google_container_cluster.target_cluster.master_auth[0].cluster_ca_certificate,)
# mgmt-console-url: deepfence.customer.com or 22.33.44.55
mgmt-console-url = "<Console URL>"
deepfence-key = "<Deepfence-key>"
image_name = "us-east1-docker.pkg.dev/deepfenceio/deepfence/cloud_scanner_ce"
image_tag = "2.3.1"
# project_id example: dev1-123456
project_id = "<PROJECT_ID>"
# region example: asia-east1
region = "<REGION_ID>"
# target gke cluster to deploy cloud scanner
cluster_name = "<TARGET GKE CLUSTER NAME>"
# target gke cluster location
cluster_location = "<TARGET GKE CLUSTER NAME>"
isOrganizationDeployment = true
# project id where the cloud scanner is deployed
deployedAccountID = "<DEPLOYED PROJECT ID>"
# organization project id
organizationAccountID = "<ORG PROJECT ID>"
}
Cloud Scanner on GCP Compute Instance
Pre-requisite:
-
GKE cluster with workload identity enabled.
(refer here for gke documentation on how to enable workload identity)
-
gcloud cli is configured and is able to access the required project where cloud scanner will be deployed
-
Install docker and docker compose on the gcp compute instance(refer docker documentation for installation instructions)
-
If an existing gcp compute instance is used, check if docker and docker compose plugins are installed on the gcp compute instance.
-
Copy and paste the following (single project or multiple projects) into a new file cloud-scanner.tf. Edit the fields: PROJECT_ID and update service account name if required.
-
Single Project Cloud Scanner on GCP compute instance with service account
data "google_client_config" "current" {}
module "cloud_scanner_example_single_project" {
source = "deepfence/cloud-scanner/gcp//examples/gce-vm"
version = "0.7.2"
# gcp service account name
name = "deepfence-cloud-scanner"
# project_id example: dev1-123456
project_id = "<PROJECT_ID>"
}
output "service_account_email" {
value = module.cloud_scanner_example_single_project.service_account_email
} -
Multiple Project Cloud Scanner on GCP compute instance with service account
data "google_client_config" "current" {}
module "cloud_scanner_example_multiple_project" {
source = "deepfence/cloud-scanner/gcp//examples/gce-vm"
version = "0.7.2"
# gcp service account name
name = "deepfence-cloud-scanner"
# project_id example: dev1-123456
project_id = "<PROJECT_ID>"
# org mode for multiple projects
isOrganizationDeployment = true
}
output "service_account_email" {
value = module.cloud_scanner_example_multiple_project.service_account_email
}
-
-
Apply the terraform script and note the service account from the output
-
Stop the gcp compute instance and update the service account in
API and identity managementselect the service account create by the terraform script and select optionAllow full access to all Cloud APIs, save the config and start the instance, if creating a new instance these options can be set while creating the instance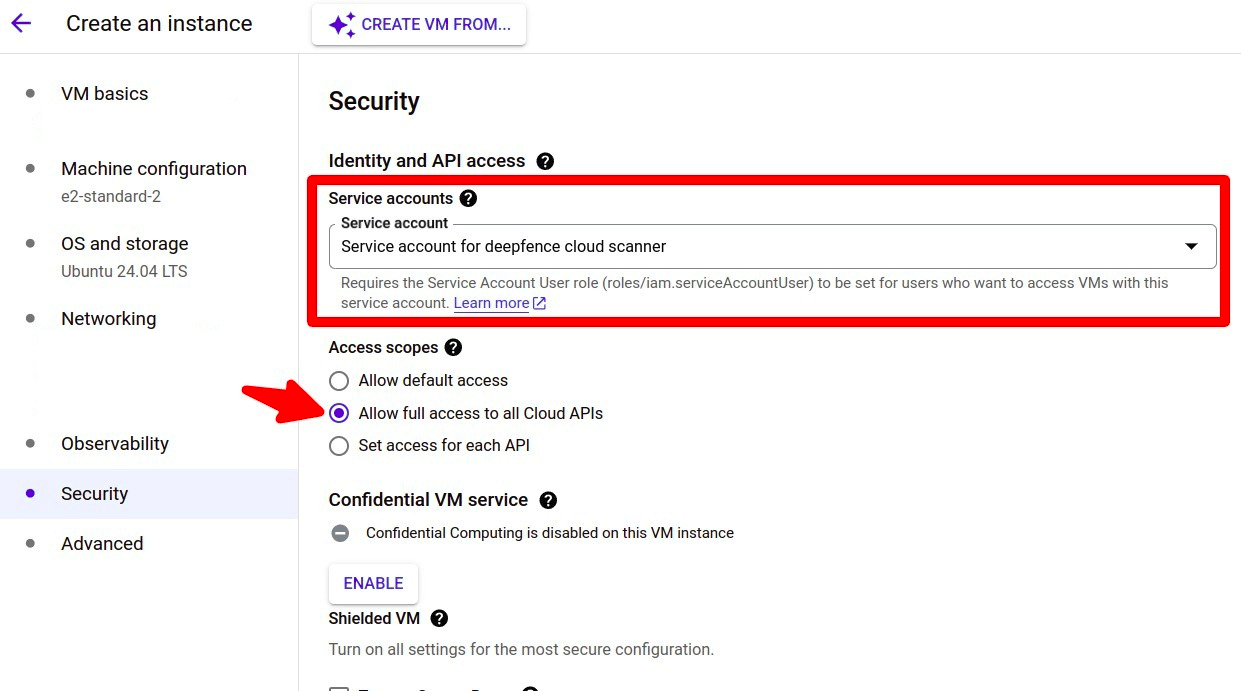
-
Create a directory deepfence-cloud-scanner and download docker-compose.yaml from the url
https://raw.githubusercontent.com/deepfence/cloud-scanner/refs/heads/release-2.3/docker-compose.yamlmkdir deepfence-cloud-scanner && cd deepfence-cloud-scanner
wget https://raw.githubusercontent.com/deepfence/cloud-scanner/refs/heads/release-2.3/docker-compose.yaml -
Update the account details and console details in the docker-compose.yaml
image: quay.io/deepfenceio/cloud_scanner_ce:2.3.1
environment:
MGMT_CONSOLE_URL: "<CONSOLE_URL>"
MGMT_CONSOLE_PORT: <CONSOLE_PORT>
DEEPFENCE_KEY: "<DEEPFENCE_KEY>"
CLOUD_PROVIDER: "gcp"
CLOUD_REGION: "<REGION>"
CLOUD_ACCOUNT_ID: "<PROJECT_ID>"
DEPLOYED_ACCOUNT_ID: "<PROJECT_ID>"
CLOUD_ACCOUNT_NAME: ""
ORGANIZATION_DEPLOYMENT: false
CLOUD_ORGANIZATION_ID: ""
ROLE_NAME: ""
CLOUD_AUDIT_LOG_IDS: ""
HTTP_SERVER_REQUIRED: "false"
SUCCESS_SIGNAL_URL: ""
DF_LOG_LEVEL: info
SCAN_INACTIVE_THRESHOLD: "21600"
CLOUD_SCANNER_POLICY: "" -
Start the cloud scanner using docker compose
docker compose up -d
What Compliance Scans are Performed?
ThreatMapper builds on a large library of controls - these are specific requirements and matching tests. For example, you will find controls that correspond to best-practice configurations of access to assets, such as enabling TLS access and blocking plain-text HTTP.
Controls are grouped into benchmarks. Where multiple benchmarks are available, controls may be used by several benchmarks.
When you run a compliance scan, you can select which benchmarks you wish to measure against, and ThreatMapper will then evaluate the appropriate controls and present the results, by benchmark, once the scan has completed.
For full information, refer to Operations: Compliance Scanning.
For maximum coverage, you can use both Cloud Scanner and local Sensor Agent compliance scans together. You could scan your GCP infrastructure using Cloud Scanner, and scan selected VMs deployed within GCP using the Sensor Agent.