The Role of ThreatMapper Sensors
Your production workloads are managed using ThreatMapper Sensors. The ThreatMapper Sensors are implemented as lightweight, privileged containers which monitor activity, discover workloads and retrieve manifests. They communicate with the ThreatMapper Management Console over TLS, using the URL and API key.
A single ThreatMapper Console can manage multiple workload types, and on-premise and cloud deployments simultaneously.
Before You Begin
Before you install the Sensors, obtain the Management Console URL and API key as described in the Initial Configuration.
You should take care to install the sensor version that matches your Management Console version, as compatibility across versions is not guaranteed.
Review the architecture for the Sensor Agent, as described in Architecture: Sensor Agent.
System Requirements
ThreatMapper performs detailed scanning of resources using sensor agents that are deployed with the target infrastructure.
Sensor containers can be deployed directly to Kubernetes or Fargate, or can be deployed on a Docker environment. If you wish to monitor a Linux-based virtual machine or bare-metal production server, you should install a docker runtime within the host Linux operating system:
| Feature | Requirements |
|---|---|
| CPU: No of cores | 0.2 units of 1 core |
| RAM | 200 MB to 1 GB |
| Linux kernel version | >= 4.4 |
| Connectivity | Access to Deepfence Management Console IP address, port 443 (configurable) |
For Windows Server hosts, experimental support exists, but it is not suitable for production use.
Installing the ThreatMapper Sensors
For your convenience, the ThreatMapper management console provides the default installation commands to install the agent on a docker host or in a kubernetes cluster:
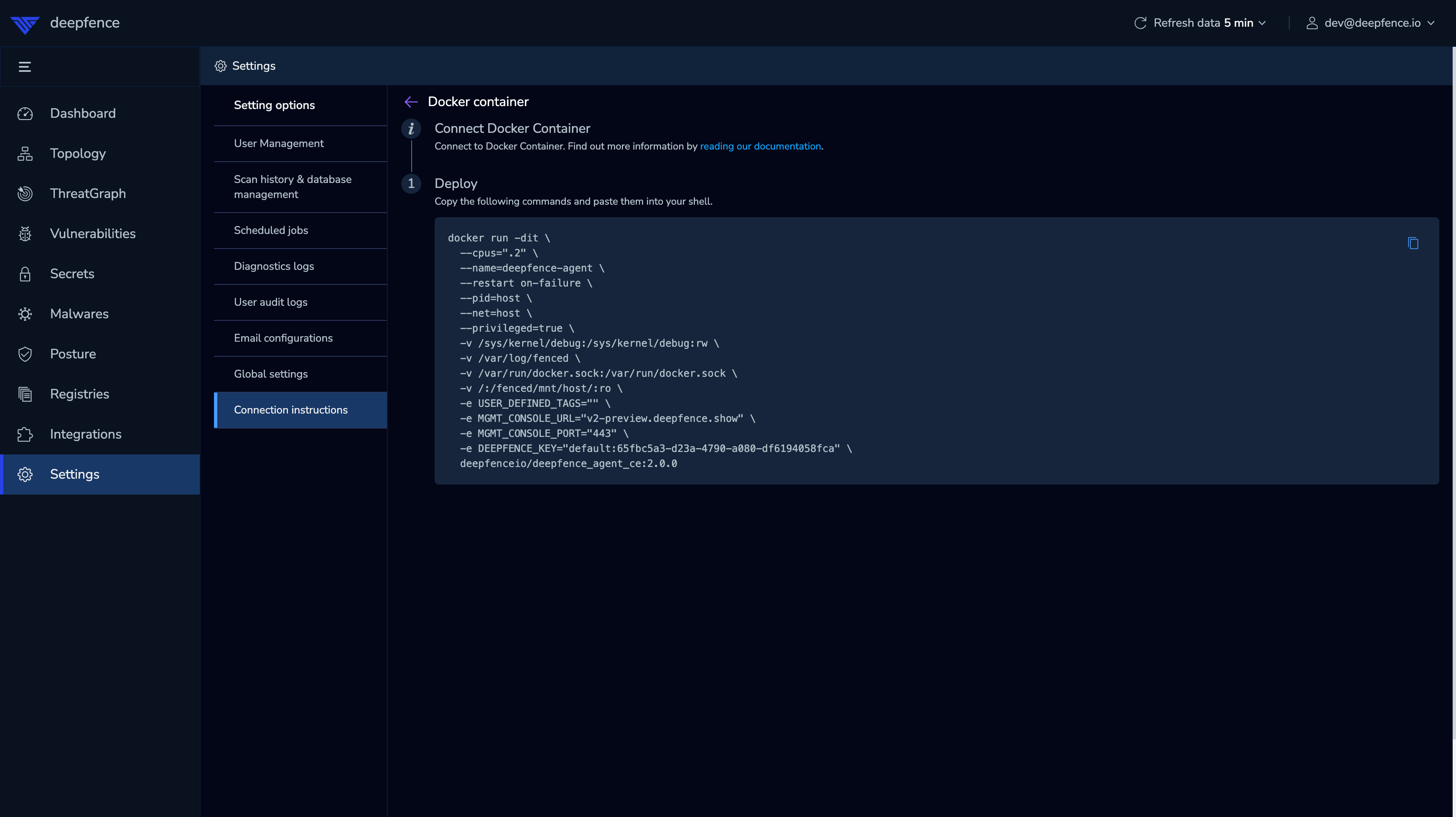 |
|---|
| Default Agent Setup (URL and Key masked) |
More detailed instructions are as follows:
📄️ Kubernetes
In Kubernetes, the ThreatMapper sensors are deployed as a daemonset in the Kubernetes cluster, using a helm chart.
📄️ Docker
On a Linux-based Docker host, the ThreatMapper agents are deployed as a lightweight container.
📄️ AWS ECS (EC2 Provider)
Deployed as a daemon service using a task definition
📄️ AWS Fargate
Deployed as a sidecar container using a task definition
📄️ Linux Host
On a Linux-based bare-metal or virtual machine workload, the ThreatMapper sensor agents are deployed as a linux binary.